The Hidden Engine of Your Digital Life
Every delayed boot, every lagging game load, and every 4K video rendering stall traces back to one critical component: your storage drive. In 2025, the SSD vs HDD debate remains pivotal as both technologies evolve. This guide dissects their differences with precision data and real-world use cases, empowering you to make an informed choice.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
Mechanical Architecture:
Imagine a high-precision turntable spinning at 5,400–7,200 RPM. Data lives on aluminum/glass platters coated with magnetic material. A physical read/write head hovers 3–7 nanometers above the surface (a human hair is 80,000nm thick).
Vulnerability Points:
Sudden movement can cause "head crash" (physical contact destroying data). Annual failure rates reach 2-5% in consumer drives due to motor wear and bearing degradation.
Energy Dynamics:
Startup power surges to 10–30W to spin platters, settling at 4–8W during operation. Heat generation: 5–10°C above ambient.
SSD (Solid State Drive)
Silicon Revolution:
Built on 3D NAND flash memory stacks (up to 232 layers in 2025). Data stored in floating-gate transistors through electron tunneling.
Controller Intelligence:
Advanced processors (like Phison E26 or Innogrit IG5666) manage wear-leveling, error correction (LDPC), and garbage collection. DRAM cache buffers accelerate small-file operations.
Power Profile:
NVMe SSDs idle at 0.05W, peak at 5–8W. No moving parts means near-silent operation and 30% longer laptop battery life.
| Use Case | HDD (SATA III) | SATA SSD | NVMe SSD (PCIe 5.0) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OS Boot (Win11) | 40–60s | 12–18s | 2.8–4.5s |
| 50GB Game Load | 90–120s | 25–40s | 6–12s |
| 4K Video Export | 35–50 mins | 8–12 mins | 90–150s |
| Random 4K Read | 0.8–1.5 MB/s | 40–90 MB/s | 350–900 MB/s |
| Latency | 7–16 ms | 0.1–0.2 ms | 0.02 ms |
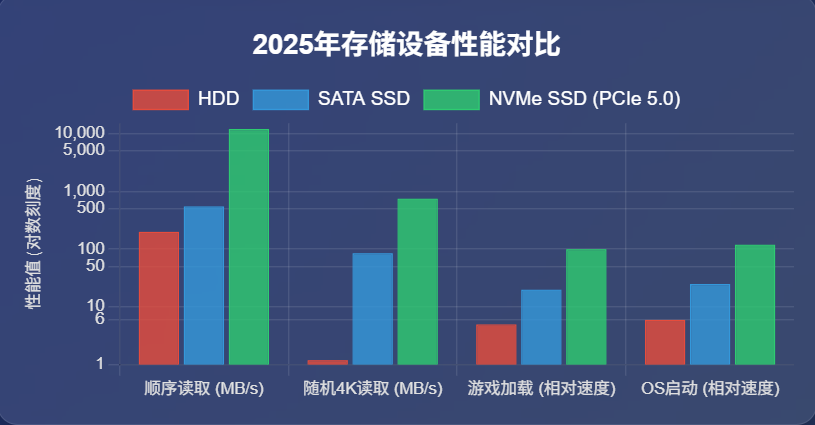
Why IOPS Matter:
HDDs manage 75–150 IOPS (I/O operations per second)
NVMe SSDs hit 1.4–2 million IOPS – critical for database workloads and 8K video editing.
Consumer Models: 22TB drives at $0.018/GB (e.g., Seagate Exos)
HAMR Tech: Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording enables 30TB+ drives by using laser-assisted writing.
Optimal Use: Cold storage, surveillance systems, RAID 5/6 arrays.
QLC/TLC Adoption: 4TB NVMe drives at $150 (QLC) vs $220 (TLC). PLC (5-bit/cell) drives emerging at $0.03/GB.
Enterprise Shift: U.2/U.3 form factors offer 30.72TB SSDs for AI training clusters.
Endurance Reality:
Drive Type TBW (Terabytes Written)
1TB HDD ~50TB (before mechanical wear)
1TB TLC SSD 600–1,200TBW
1TB QLC SSD 200–360TBW
Physical Stress: 70% of portable HDDs fail within 3 years due to shock/vibration.
Environmental Limits: Operates safely at 5–55°C. Humidity >80% risks platter corrosion.
Write Amplification: Controller efficiency reduces unnecessary writes (WAF 0.5–1.5 in modern SSDs).
Data Retention:
10+ years at 25°C
Drops to 1 year at 40°C (QLC)
TRIM & Over-Provisioning: Self-maintenance preserves performance over time.
Ideal Setup: 2TB PCIe 5.0 SSD (e.g., WD Black SNX) + 32GB RAM
Why NVMe?: DirectStorage API enables GPU-to-SSD data streaming, cutting load times by 60%.
Render Tests: DaVinci Resolve 8K timeline scrubbing:
HDD: 3–7 fps
NVMe SSD: 24–48 fps
Tiered Storage:
Tier 1: 500GB SSD cache (ZFS L2ARC)
Tier 2: 4x 18TB HDDs (RAID 10)
Power Savings: Replacing 4 HDDs with SSDs cuts 40W/hour (~350 kWh/year).
Laptop SSD Advantages:
Shock resistance survives 1,500G impacts (vs HDD’s 300G limit)
Weight savings: 70g vs 120g (2.5" HDD)
Best Pick: M.2 2230 NVMe (e.g., Sabrent Rocket Nano) for ultraportables.
SSD Innovations:
Z-NAND: Low-latency niche drives (10μs access time)
Computational Storage: SSDs with onboard FPGA for real-time data processing.
HDD Renaissance:
HAMR+: Multi-actuator tech doubles throughput to 1GB/s
Glass Substrates: Enable 50TB+ capacities by 2027.
Emerging Tech:
Optane Successors: 3D XPoint 2.0 for persistent memory tiering
DNA Storage: Experimental 1EB/g density (not commercial yet).
Adopt This Hybrid Strategy in 2025:
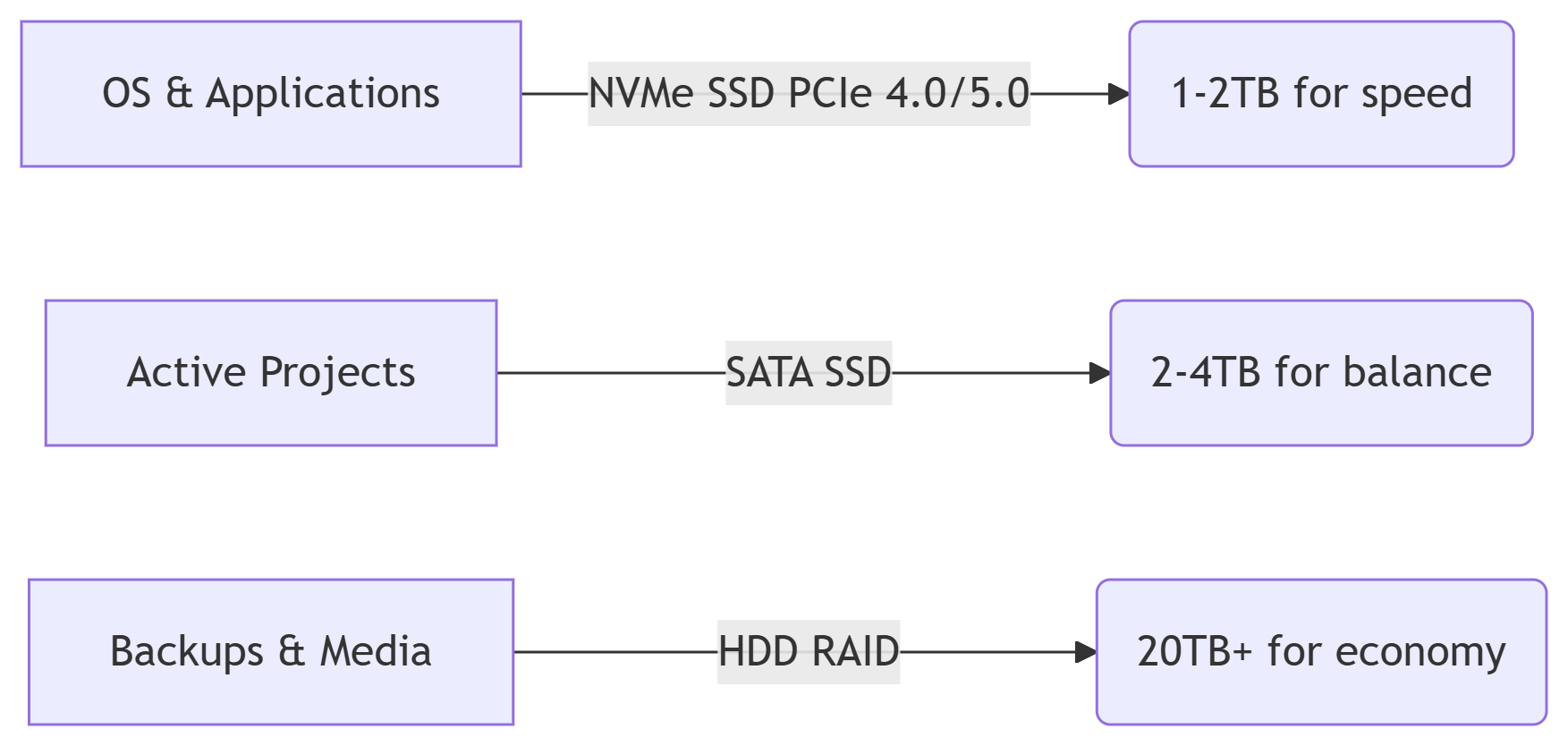
Final Recommendations:
Priority: Speed → PCIe 5.0 NVMe SSD (e.g., Crucial T705)
Priority: Capacity → 22TB HDD (e.g., WD Gold)
Balanced Budget → 1TB NVMe + 8TB HDD ($180 total)
At BVS, we specialize in developing and manufacturing high-performance industrial embedded computers. Our product range includes rugged embedded box PCs, fanless industrial computers, and custom embedded solutions designed for various industries. We focus on creating reliable, high-performance systems that withstand harsh industrial environments. Whether it's a compact embedded PC for space-constrained applications or a powerful industrial computer for complex data processing tasks, we have the expertise to deliver tailored solutions that meet the unique requirements of real-time data processing in industrial settings.

Click to confirm
Cancel